What does data of a million football games tell us?
DATA - By digging through the basic data of one million football (soccer) games, going back to 1901, you can distill some interesting trends. The average goals scored per game is 2,77. But there’s a lot more to it.
Courtesy of the people of Footballfans.eu, a groundhopping community, I was able to analyse the outcomes of a million football games. The oldest games are from the English First Division in 1901. The database now contains competitions and cups from over 75 countries and most international championships. It’s a wealth of data, that shows for instance that the home game advantage has been declining over time. Or that players in the northern hemisphere score more goals during the summer, but players in the southern hemisphere do not. And that Morocco is the country where the least goals are scored on average.
But first, let’s look at the distributions of the scores from all the games in the data set. As you can see, 1-1 is the most common score, 11 percent of the games end that way after regular playing time.
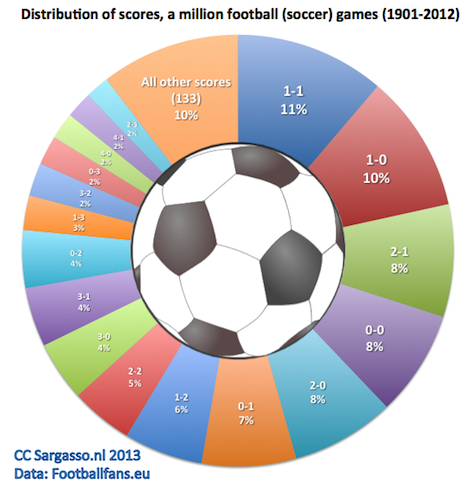
In the section “other scores”, we find some pretty exotic results. How about 0-31 in the game between Snæfell and Haukar in Iceland? Or 24-0 in a game in Estonia between Levadia and FC Soccernet? Also worth mentioning are two very old friendly games. In 1908 Denmark defeated France with 17 to 1! More recently in 2011 San Rafael lost to Atlético Madrid with 1 to 19.
